[애니멀피플] What happened to the ‘Appspider Spider Web’ experiment started in the 70s
Difficulty in food procurement, distinction between male and female … Space experiment unexpected hurdle ‘
By the 2010s, after repeated trial and error, the direction with light was detected
A mitigation spider that created a web in zero gravity at the 2011 International Space Station (ISS) test site. Biosb Space Technology is provided by the University of Colorado’s Boulder campus.
Can spiders spin webs at external locations without gravity? Answering these questions has been a popular project, among experiments conducted on the space station. However, the project launched in the 1970s to promote space exploration and contribute to science education was not very successful. Contrary to grand propaganda, how little the spider web on the ground differs from the cosmic web is known by very few people. Researchers participating in this project finally came up with the results of the experiments conducted so far. In a paper published in the latest issue of the scientific journal ‘Science of Nature’, researchers reported unpredictable spider behavior that they discovered among small accidents occurring one after another.
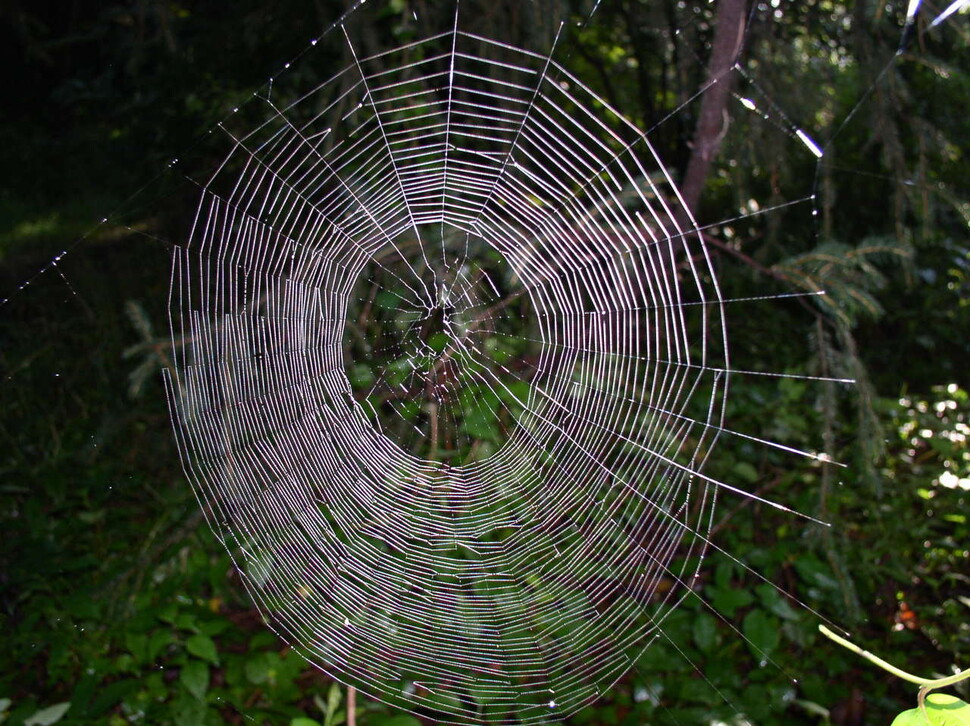

Magician Spider web. The center is slanted upward compared to the center of the spider web, and the lower section is denser and the area wider. Beatrice Moose, provided by Wikimedia Commons.
On the ground, the spiders spread their webs straight to the ground to catch flying insects. If you look closely, the center of the web is not in the middle, but slightly above it. When you think of hunting for food, it is easy to see why. This is because when a spider gets a worm in its web, it jumps down fast and hits the body using gravity instead of climbing the web. To do this, the bottom of the web has to be widened, and it will naturally become an asymmetrical shape that tilts upward from the center. Then, what kind of spider web would be in outer space without gravity? Since there is no gravity to use, it will be a symmetrical type with the center of the spider web in the middle. Furthermore, spiders on the ground always have their heads in the direction of gravity, and if they are caught, they quickly attack them, but there will be no direction in outer space.
_______
A series of mistakes
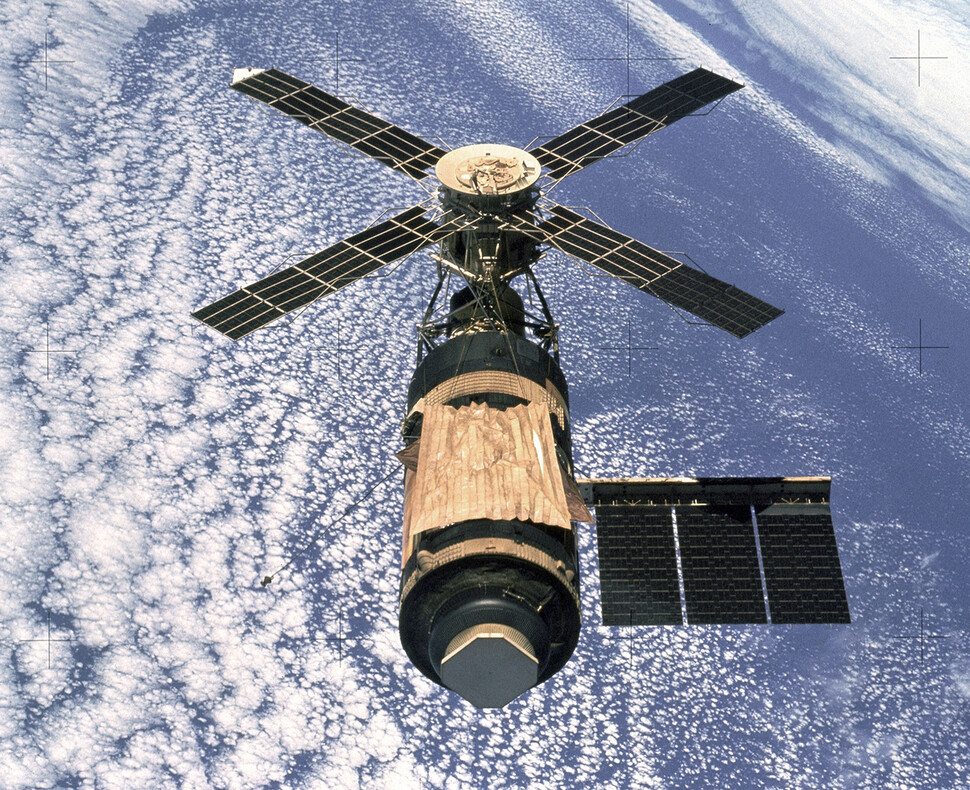

Skylab, a space station, was launched and operated by NASA in 1973. Space Spiders were also aboard at this time. Screws provided.
To test this hypothesis in outer space, a spider was placed on a spacecraft. The first attempt was Skylab, the first space station launched and operated by NASA in 1973. The first Space Spider was born with this proposal in a high school students science competition. It was a brilliant idea, but the preparation and experimentation were poor. I left 5 pictures of spider webs, one of which had a symmetrical shape, and the rest had irregular spacing or small web sizes. It was confirmed that ‘the spider could kill the spider webs in space’, but it was not clear whether the size was due to weightlessness. This was because it was difficult for the spiders to live before the webs of the spiders as they did not prepare water and food to eat.

NASA is using and using educational materials for science teachers about spiders trapping in outer space. (Noori House: https://www.bioedonline.org/lessons-and-more/teacher-guides/spiders-in-space/)
The second experiment was carried out at the International Space Station (ISS) in 2008. This time, he also took fruit flies for a spider meal. A spider of a different species was placed in every two kennels, just in case. The first accident was that a spider somehow got into the main feedlot from the reserve feedlot. The first spider hit a nice symmetrical web within six days of arrival, but an hour later, the invading spider hit its own web and became engrossed. This time, hunting caused problems. Fertility of fruit flies was underestimated. The larvae and pupae of fruit flies increased rapidly, after one month, the observation window was completely blocked. Re-experimenting with spider webs at the International Space Station in 2011, Samuel Choker of Switzerland and Dr. The University of Basel introduced a new examination method to avoid repeat failure. First, a mitigation spider, which collides with the most heterogeneous traps on the ground and can easily block its direction due to its elongated body, was chosen as the target species, and then an experimental one with similar conditions Equipment that excludes gravity and the ground station was set up for comparison.
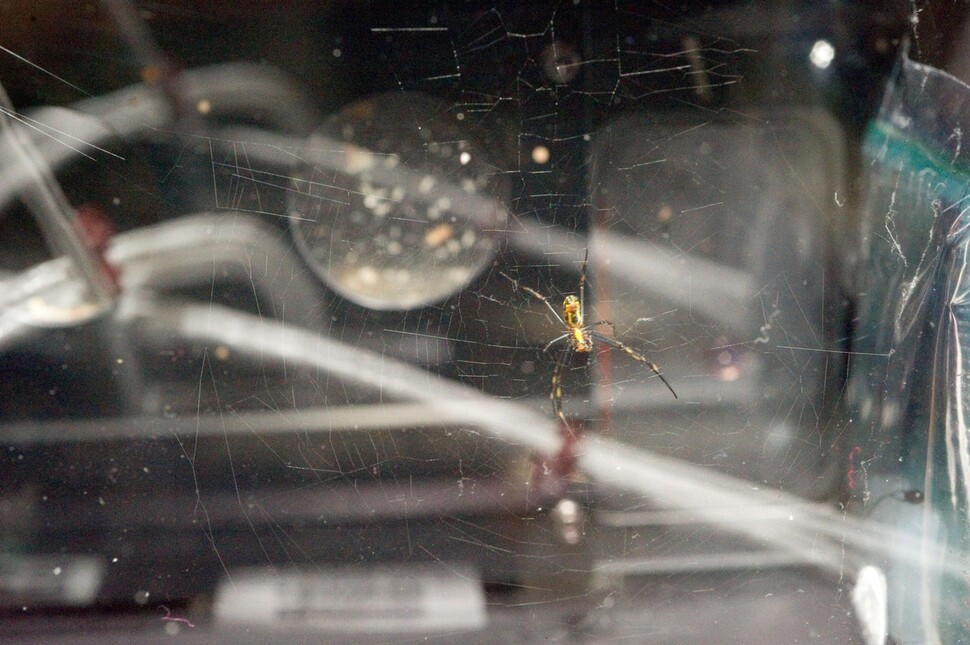

At the Biosob Space Technology Laboratory at the University of Colorado’s Boulder Campus in the United States, a space station and an experimental site with the same conditions except gravity were built and studied for comparison. Screws provided.
Three cameras were placed and action was taken every 5 minutes for two months. Space spiders were collected at the Kennedy Space Center and then carefully selected four young females (a few accidents occurred here, two later turned out to be male instead of female. Male and female spiders are very difficult to cover when they Are smaller). It is difficult, fortunately, the men were placed separately on the ground and in space).
_______
Light without gravity

An experimental device for radish cultivation on the International Space Station. Screws provided.
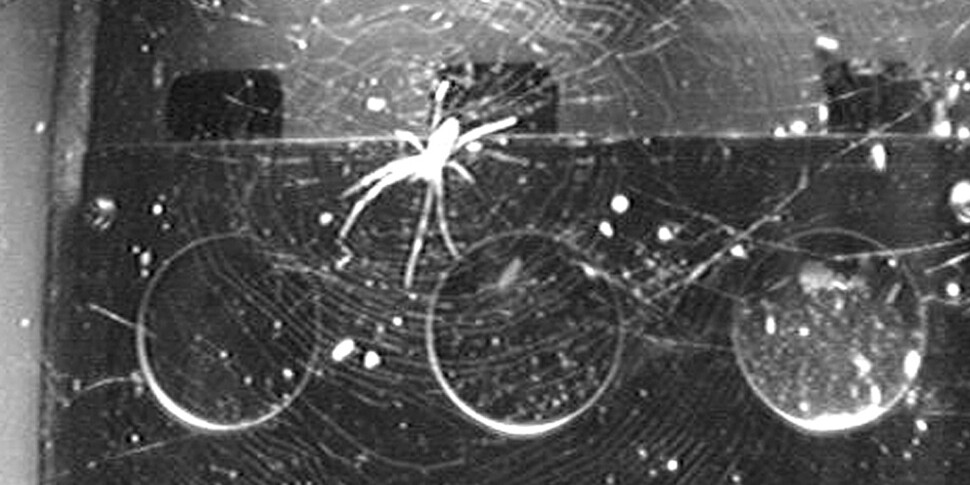
Anyway, the experiment was successful, and 14,500 spider webs and orientation photographs were secured. Now, the space spider is perfectly round and collides with a spider web that sits in the center, and the head of the spider sitting there is in an irregular direction? Unfortunately, this was not the case. The researchers said, “The webs in zero gravity were more symmetrical than those on the ground, and the center was closer to the center. The spider’s head was not always facing downward.” At the test site, every 12 hours The lights were turned on and off, but the space spider behaved only as expected in zero gravity, while the lights were turned off, and when the lights turned on, it showed similar behavior as the ground. The lead author, Drs. Choker said, “We didn’t even dream that the light in space would dominate the spiders. It’s a good idea because the light was only attached to the top of the experiment site. I almost couldn’t do it.” In this university press release said.
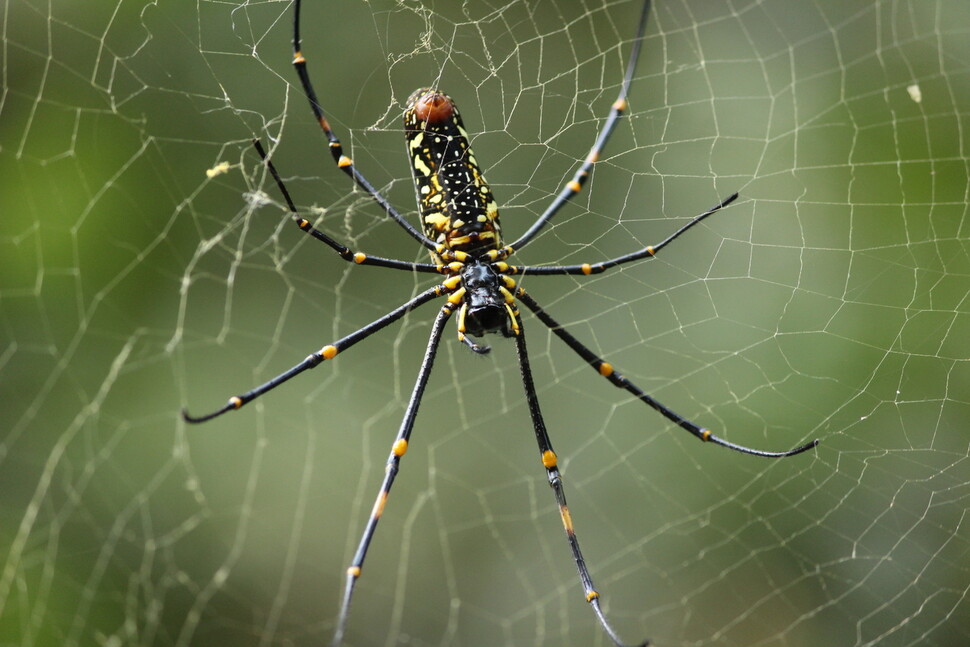

A magician spider experimented with spider webs on the International Space Station. It turns out that without gravity, it is the ability to orient light. Provided by Wikimedia Commons.
Previous studies have shown that spiders make webs and catch their prey even in complete darkness without any light. Therefore, for spiders, light was considered an insignificant factor. However, as gravity disappeared from the outer space, the spider relies on light to orient itself. When the light was turned off, I set the direction arbitrarily, but when the light was turned on, I turned the other side of the light. Dr. “It is amazing that spiders have a system that directs light instead of gravity, even though they have never experienced a gravity-free environment in their evolution,” Choker said. The shaman spider who participated in this experiment also produced several new records. After setting a record for 65 days of living in space, the male returned safely to Earth, and the female made 34 spider webs in space and set off her skin three times. Quoted Letter: Science of nature, DOI: 10.1007 / s00114-020-01708-8 by Cho Hong-sip, staff reporter [email protected]
