


A new rover built by Nasa and named Perseverance will land on Mars in February 2021 working with the “sky crane” strategy. A large parachute and rocket motors will gradual the mission’s descent before the rover is lowered to the area using cables.
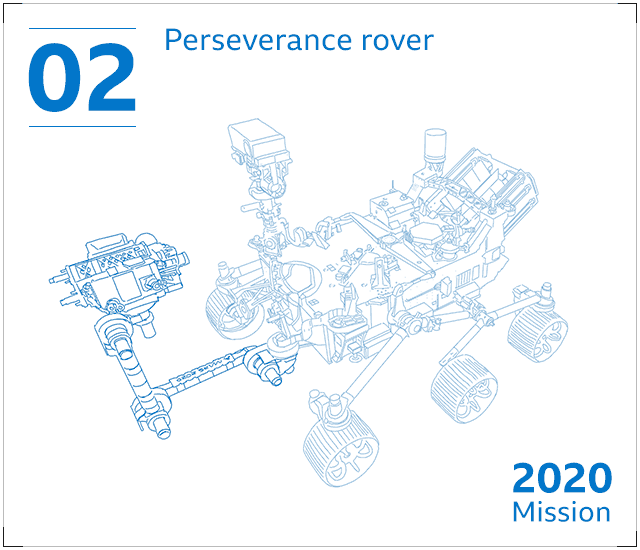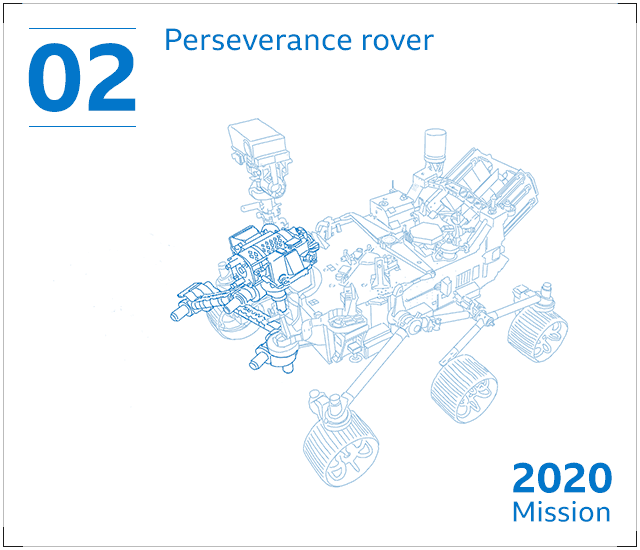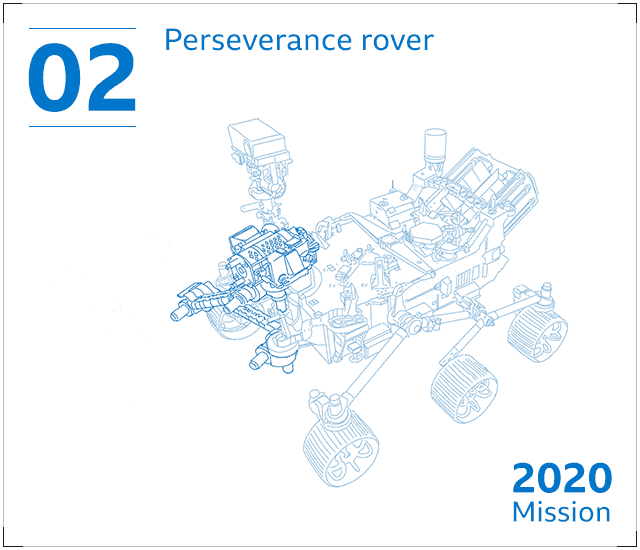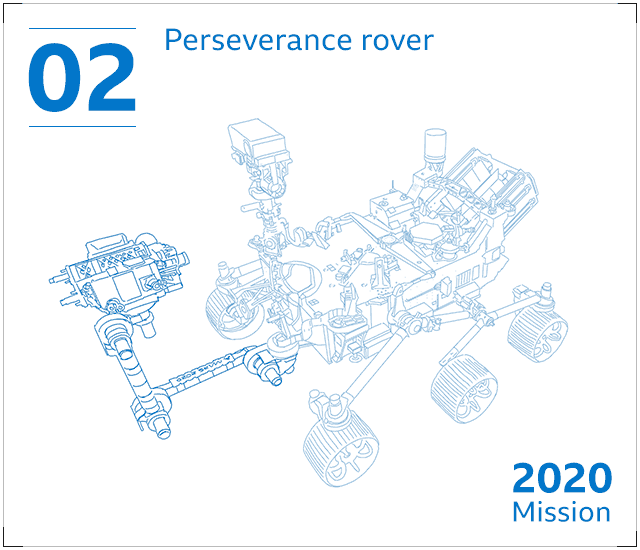
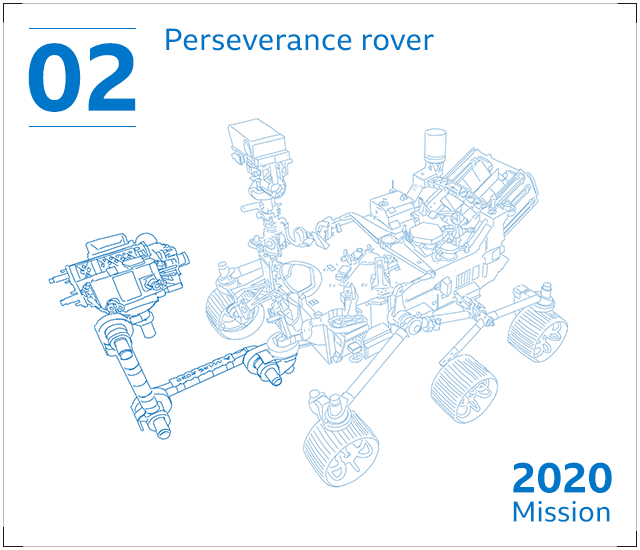
Perseverance – a six-wheeled robotic machine with 23 cameras and a drill – will seek signs of historical lifestyle in a massive crater Jezero. It will collect rock and soil samples that seem like they may possibly have been altered by make contact with with microorganisms.
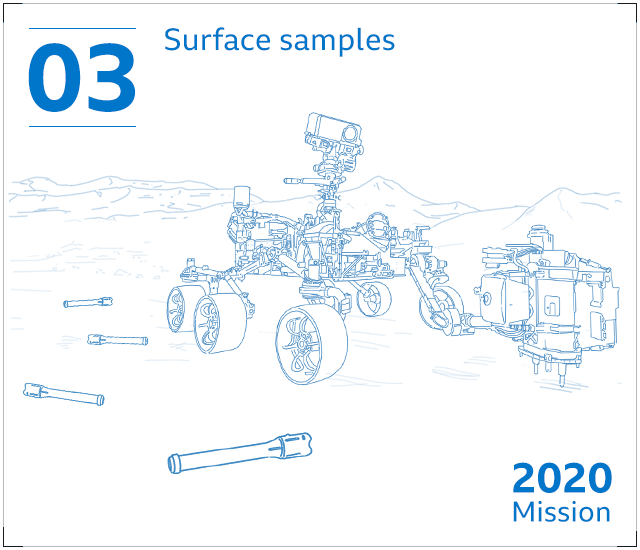
The rover will retail store its samples in metal canisters – but depart them at the rear of on the Martian surface to continue its mission. Perserverance’s plutonium-based mostly power offer could keep the rover trundling close to Mars for 10 many years or much more.
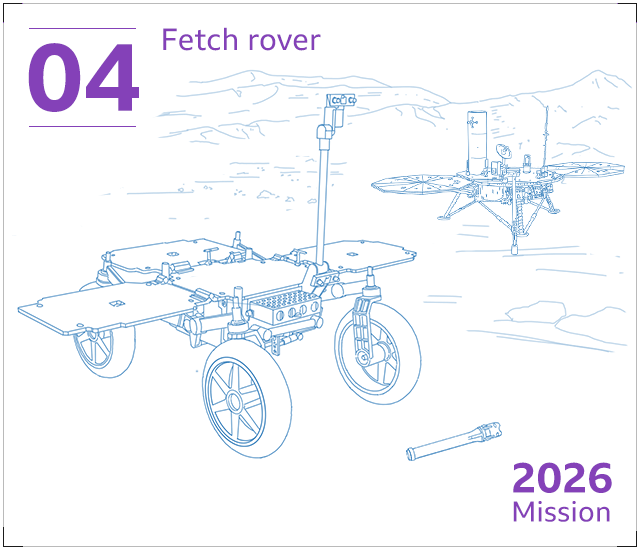
Later this ten years – just after 2026 – a next, lesser rover, to be built by the European Space Agency (Esa), will arrive on Mars. This “fetch rover” will vacation across the floor finding up the sample canisters remaining guiding by Perseverance.
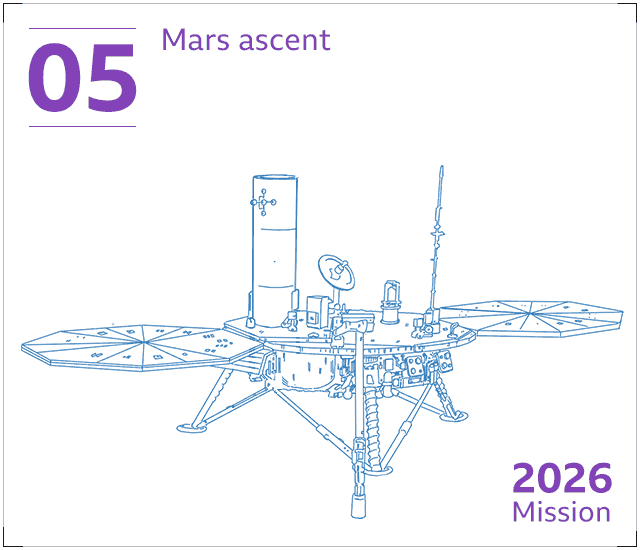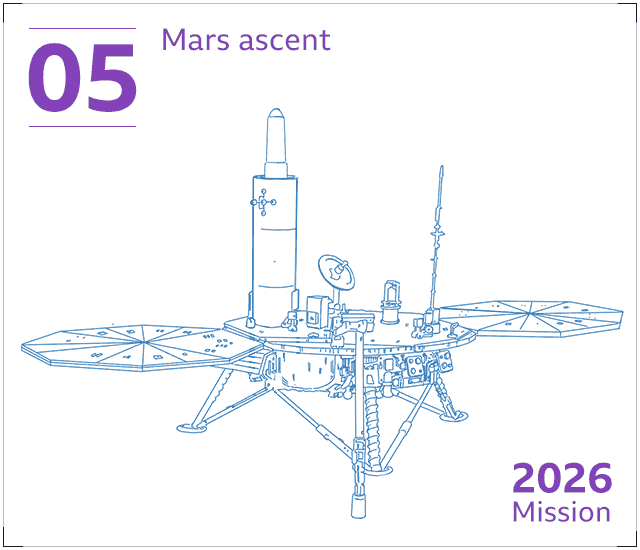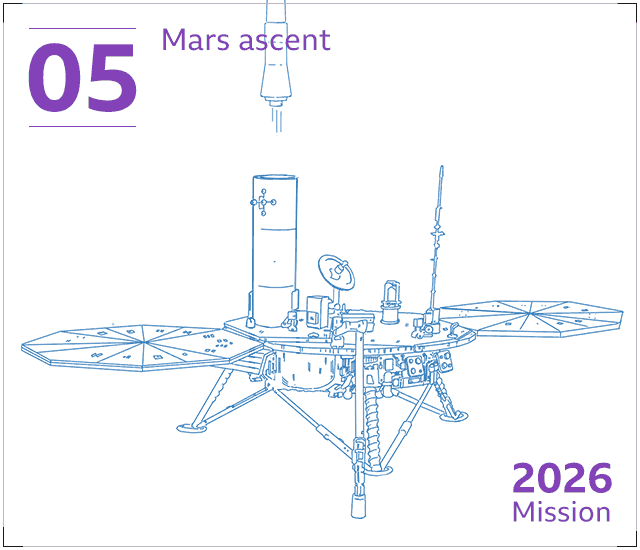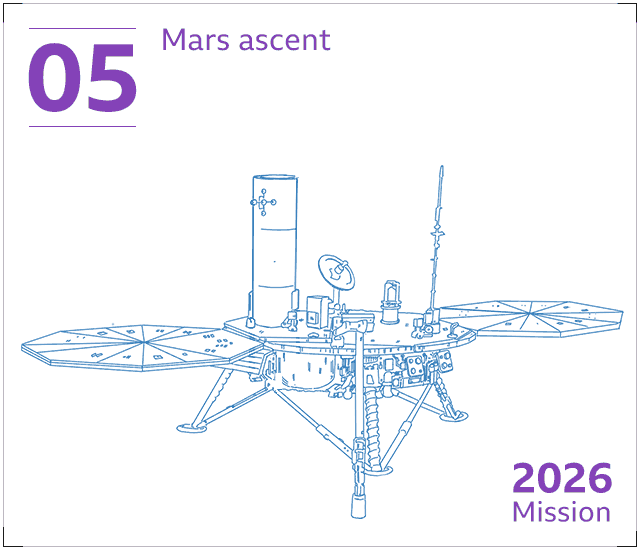
The canisters will be loaded into a protective container and put into a compact rocket – the Mars Ascent Automobile or MAV. This will blast into the sky, inserting the container into orbit all-around Mars.
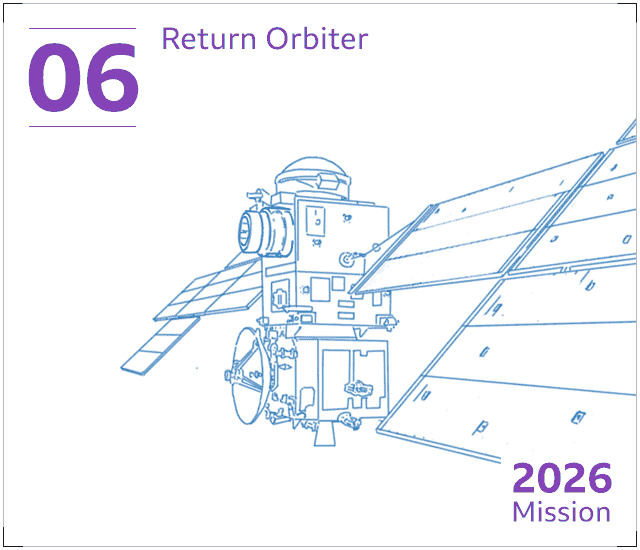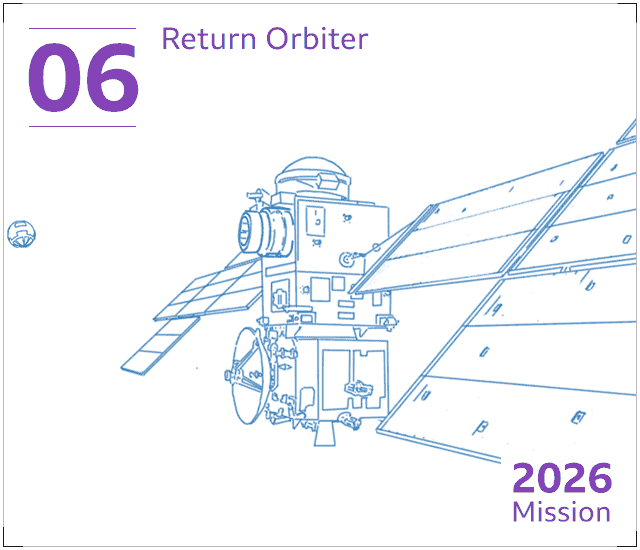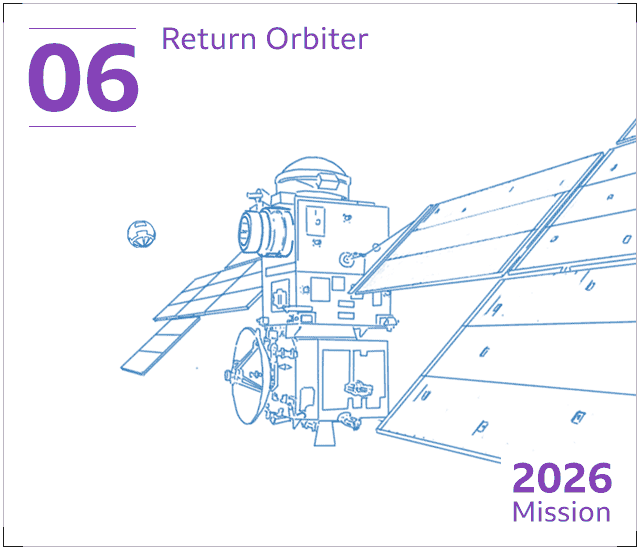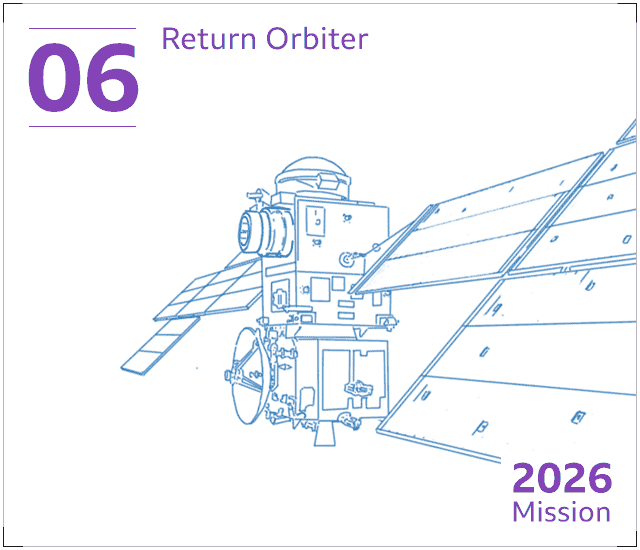
The sample container will be fulfilled in orbit and caught by a European satellite. This “return orbiter” will act like a cargo ship, bringing the treasured rock and soil specimens back again to Earth.
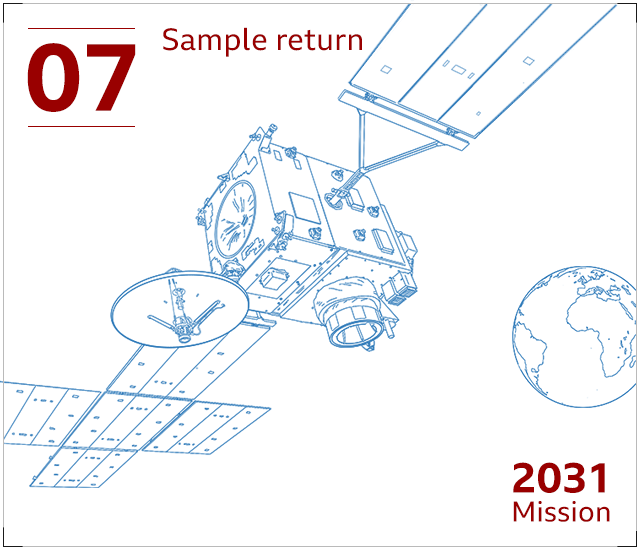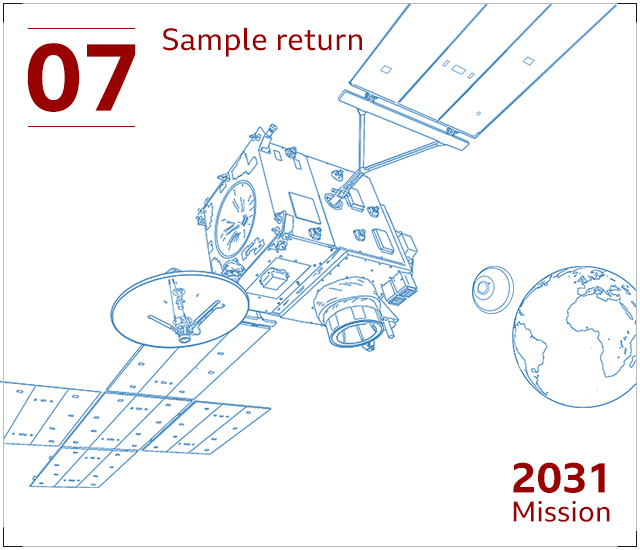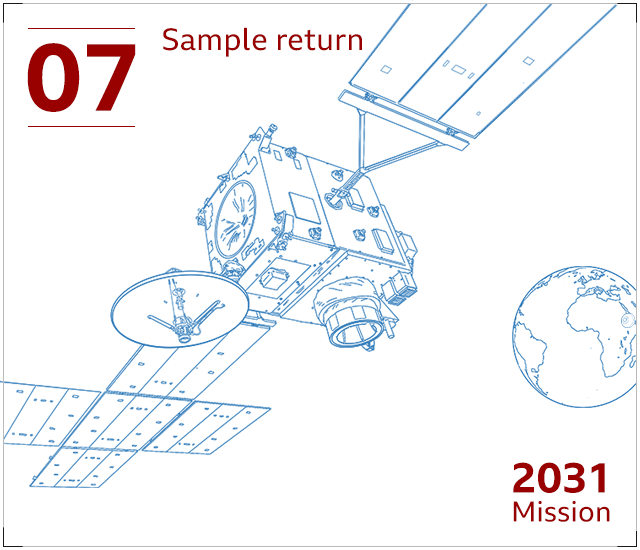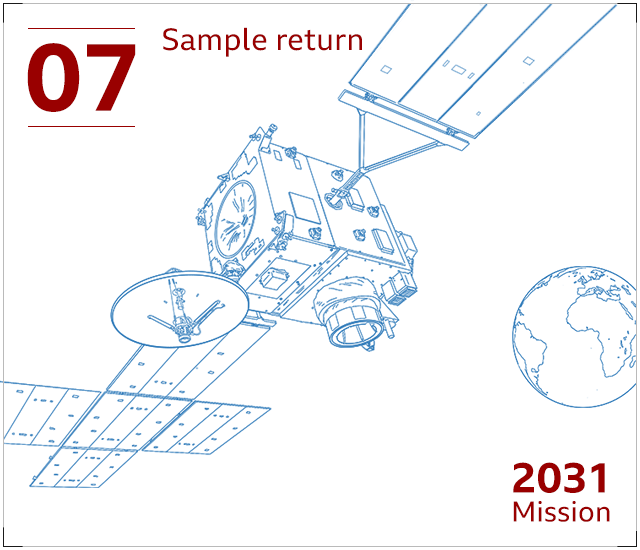
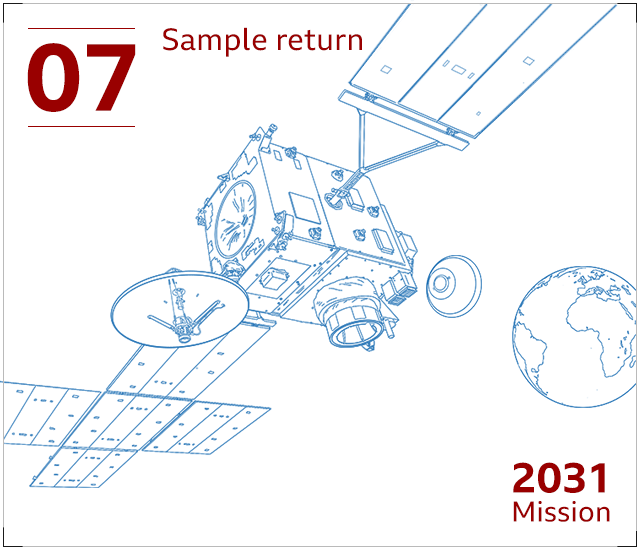
We do not count on the satellite to get there property until eventually at minimum 2031, by which time the sample container will have been packaged in a intensely secured capsule, to be despatched into Earth’s ambiance to land in North The usa.
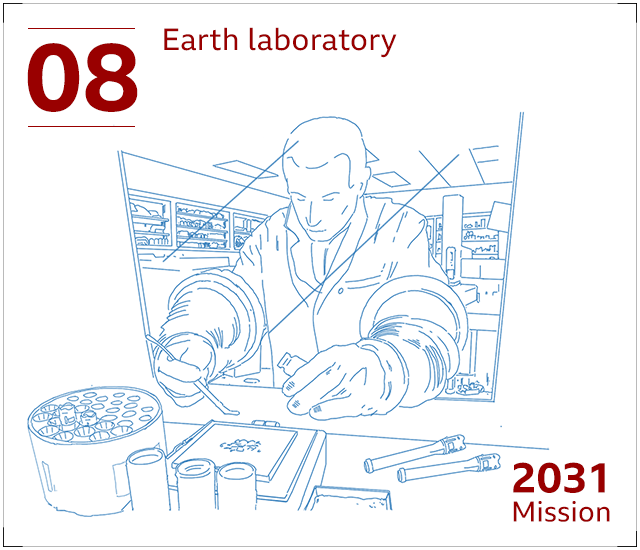
Experts will then review the rocks and soil working with advanced strategies, like some that have still to be invented simply because there should really be plenty of product to investigate for many years in advance. The samples will shed mild on Mars’ history and no matter if it has at any time supported microbial lifeforms.
